What Is Lupus? Understanding the Autoimmune Disease Basics

What Is Lupus? Understanding the Autoimmune Disease Basics. Lupus is a complicated and often misunderstood autoimmune disease. Let’s break it down to help you understand what it is, what causes it, and how it can be managed.
Understanding Autoimmune Diseases
How Autoimmune Diseases Work?
In autoimmune diseases, the immune system mistakenly attacks the body’s tissues. Normally, the immune system defends against infections, but in disease, it targets healthy cells, leading to inflammation and damage.
Lupus as an Autoimmune Condition
Lupus is one of the most complex autoimmune diseases because it can affect multiple systems in the body, including the skin, joints, kidneys, heart, and brain.
Types of Lupus
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE)
This is the most common and severe form of this disease, affecting various organs and tissues.
Cutaneous Lupus
This type primarily affects the skin, causing rashes and lesions, often triggered by sunlight.
Drug-Induced Lupus
Certain medications can cause this disease-like symptoms. These typically resolve after the medication is discontinued.
Neonatal Lupus
A rare condition where a mother with this disease passes certain antibodies to her baby, causing temporary symptoms in the newborn.
Causes of Lupus
Genetic Factors
People with a family history of this disease are at a higher risk, although no single gene is responsible.
Environmental Triggers
Exposure to sunlight, infections, and certain medications can activate this disease in susceptible individuals.
Hormonal Influences
Women are far more likely to develop this disease, suggesting that hormones like estrogen play a role.
Search for Health: Is Pneumonia Contagious and Is Bronchitis Contagious?
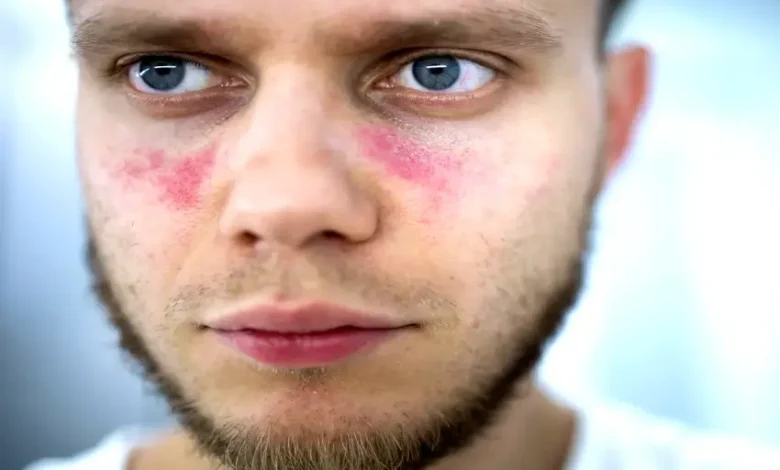
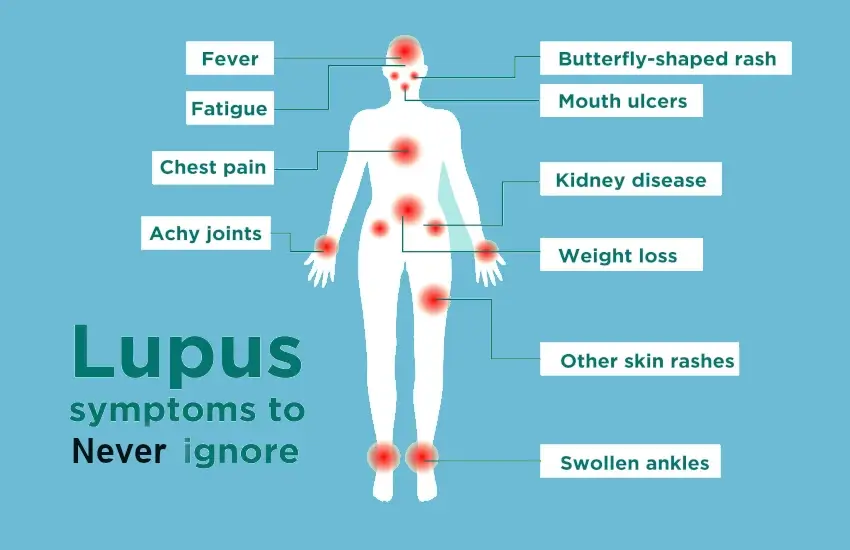
Symptoms of Lupus
Common Symptoms
- Fatigue
- Joint pain and swelling
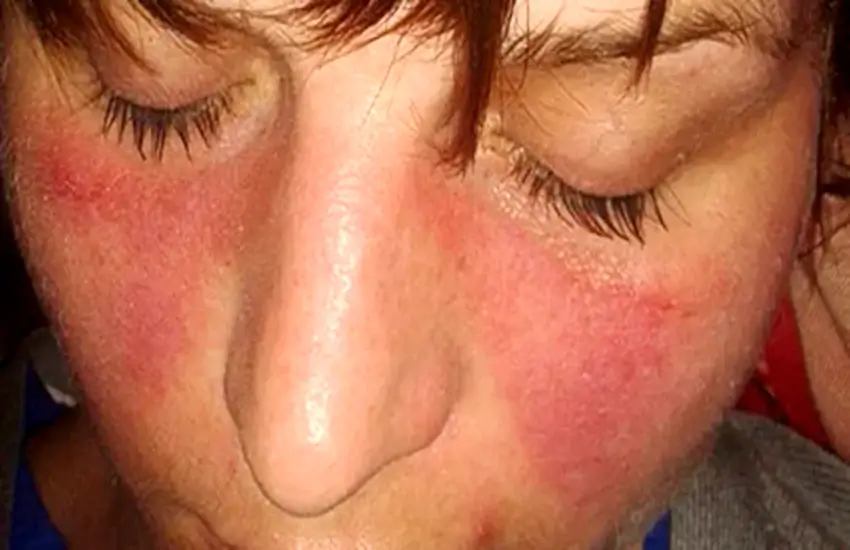
- Butterfly-shaped rash across the cheeks and nose
- Fever
Organ-Specific Symptoms
- Kidney issues, such as this disease nephritis
- Heart complications, like inflammation of the heart lining
- Neurological symptoms, including headaches and seizures
How Lupus Is Diagnosed?
Medical History and Physical Exam
Doctors will review symptoms and check for signs like rashes, swelling, and joint pain.
Diagnostic Tests
Tests such as ANA (antinuclear antibody) and other blood or urine analyses help confirm the diagnosis.
Treatment Options for Lupus
Medications
- Anti-inflammatory drugs: For pain and swelling
- Immunosuppressants: To calm an overactive immune system
- Corticosteroids: For managing severe inflammation
Lifestyle Adjustments
- Maintain a healthy diet and exercise routine.
- Avoid excessive sunlight and stress.
Living with Lupus
Managing Flare-Ups
Flare-ups can occur unpredictably, so recognizing early warning signs and adjusting your routine is vital.
Emotional and Mental Well-Being
Dealing with this disease can be overwhelming. Support groups, therapy, and mindfulness practices can make a big difference.
Risk Factors and Who Is Affected
Gender Differences
This disease predominantly affects women, particularly during childbearing years.
Ethnic Background
People of African, Hispanic, Asian, and Native American descent are more likely to develop this disease.
Family History
A family history of autoimmune diseases increases the likelihood of this disease.
Myths About Lupus
- Myth: This disease is always fatal.
- Fact: With treatment, most people live normal lives.
- Myth: this disease only affects women.
- Fact: Men can develop this disease too, although it’s less common.
How Lupus Differs from Other Autoimmune Diseases?
Unlike rheumatoid arthritis or multiple sclerosis, this disease can affect multiple systems simultaneously, making it harder to diagnose and treat.
Lupus and Pregnancy
Challenges for Expectant Mothers
Pregnancy with this disease requires close monitoring to prevent complications like preeclampsia or preterm birth.
Managing Lupus During Pregnancy
With proper care and adjustments to treatment, many women with this disease have successful pregnancies.
Research and Future Treatments
Ongoing research aims to develop more effective medications with fewer side effects. Biologic drugs and personalized medicine show promise in improving outcomes.
Support and Resources
Organizations like the This Disease Foundation of America provide resources, support groups, and advocacy for patients and their families.
Conclusion
Lupus is a complex condition that affects every individual differently. By understanding its causes, symptoms, and treatment options, those affected can take control of their health. Remember, early diagnosis and proper care make a significant difference in managing this disease effectively. For more Health Tips visit our Website Media Music Mania.
FAQs
1. What triggers lupus flare-ups?
Common triggers include stress, sunlight, infections, and certain medications.
2. Is lupus hereditary?
While there’s a genetic component, having a family history doesn’t guarantee you’ll develop this disease.
3. Can lupus go into remission?
Yes, with effective treatment, many patients experience periods of remission where symptoms are minimal or absent.
4. What’s the difference between lupus and rheumatoid arthritis?
This disease can affect multiple organs, while rheumatoid arthritis primarily targets the joints.
5. How long can someone live with lupus?
With advancements in treatment, most people with this disease have a normal or near-normal lifespan.